The Economics and Statistics Division maintains archives of previous publications for accountability purposes, but makes no updates to keep these documents current with the latest data revisions from Statistics Canada. As a result, information in older documents may not be accurate. Please exercise caution when referring to older documents. For the latest information and historical data, please contact the individual listed to the right.
<--- Return to Archive
For additional information relating to this article, please contact:
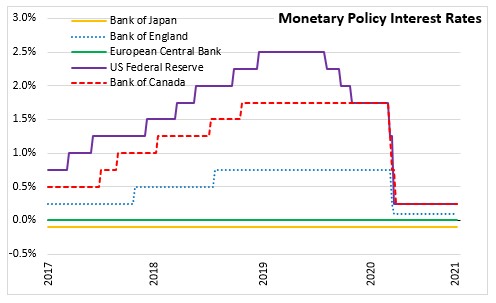
January 21, 2021EUROPEAN CENTRAL BANK MONETARY POLICY The European Central Bank announced today that key interest rates would remain unchanged at their current levels given the need to continue monetary policy stimulus to support economic recovery and price stability. They are expected to remain at their present or lower levels until the inflation outlook converges to a level sufficiently close to, but below the target rate of 2 per cent consistently.
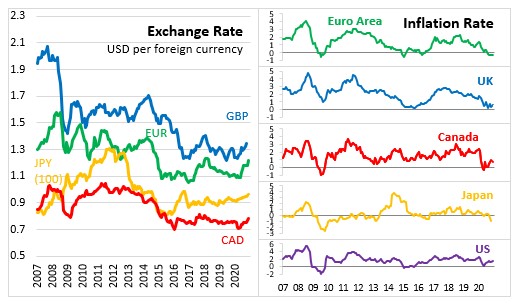
Economic activity in the Euro Area increased 12.4% from the previous quarter in Q3 following a sharp contraction in the first half of 2020. Despite the rebound in economic conditions, activity in the third quarter remains below pre-pandemic levels. Recent economic indicators signal a decline in the economic activity in the fourth quarter of 2020 due to the impacts of the second wave of the pandemic and the associated containment measures.
Recovery continues to be uneven across sectors with industries relying on face-to-face interactions falling behind in recovery. While fiscal stimulus measures are providing support to businesses and households, confidence remains low.
The COVID-19 vaccine roll-out which started in late December 2020 is providing greater confidence in the resolution of the health crisis. However, the ECB expects that widespread immunity will take some time. As such, the recovery of the euro area economy needs to be supported by favourable financing conditions, an expansionary fiscal stance and a recovery in demand over the medium term as containment measures are lifted.
While the upward trend in global economic conditions, the agreement on future EU-UK relations, and the start of vaccine roll-out provide more certainty, the risks around the euro area economic outlook still remain on the downside.
Against this background, the Governing Council reconfirmed its accommodative policy stance. The measures in place include:
- Continuation of net asset purchases under the pandemic emergency purchase programme (PEPP) with a total envelope of €1,850 billion until at least the end of March 2022. The net purchases will continue until the COVID-19 crisis is over.
- Continuation of the reinvestment of principal payments from maturing securities purchased under the PEPP until at least the end of 2023.
- Continuation of net purchases under asset purchase programme (APP) at a monthly pace of €20 billion. Monthly net asset purchases are expected to run for as long as necessary to reinforce the accommodative impact of the policy rates, and shortly before any increase in the key ECB interest rates.
- Continuation of the third series of targeted longer-term refinancing operations (TLTRO III). These conditions will be offered only to banks that achieve a new lending performance target in order to sustain the current level of bank lending.
The December 2020 Eurosystem staff macroeconomic projection’s baseline scenario forecasts real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to decline by 7.9% in 2020 followed by 3.9% growth in 2021. Economic growth is projected to rebound to 4.2% in 2022 and than slow down to 2.1% in 2023. The December 2020 projections over the short term represent a small downgrade from the September 2020 ECB staff macroeconomic projections.
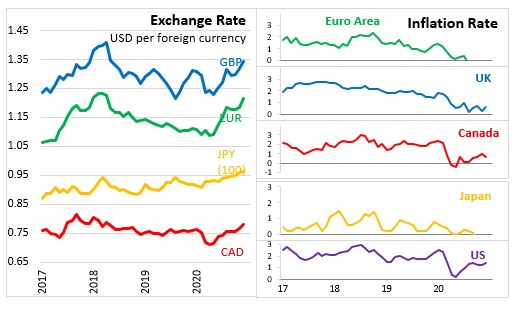
The Eurostat flash estimates show that annual inflation in the Euro Area remained unchanged at -0.3% in December 2020. Given the soft energy prices and the ending of a temporary reduction in the German VAT rate, inflation is expected to increase over the next months. The December 2020 ECB staff projections see annual inflation at 0.2% in 2020 before increasing to 1.0% in 2021. Inflation is expected to gradually increase to 1.1% in 2022 and 1.4% in 2023. However, the December projections for inflation in 2020 and 2022 represent a downgrade from the September 2020 projections.
While the prospects of an effective vaccine roll-out provides more confidence that the health crisis will gradually resolve, the recovery of economic activity in the Euro Area needs to be supported by favourable financing conditions over the short term. Overall, the Governing Council noted that an ample degree of monetary accommodations is necessary to support economic activity and the robust convergence of inflation to levels that are below, but close to, 2 per cent over the medium. In addition, an ambitious and coordinated fiscal stance remains critical, in view of the sharp contraction in the euro area economy and the reduction in private demand.
The Governing Council noted that the monetary policy measures announced today are expected to sustain favourable financing conditions over the pandemic period and support the flow of credit to all sectors of the economy.
The Governing Council also noted that the Next Generation EU package has an important role in supporting a faster, stronger, and more uniform recovery among Member States. The Governing Council reconfirmed their stand to adjust the monetary policy instruments as needed to ensure that inflation moves toward the target rate in a sustained manner.



Source: European Central Bank: Monetary Policy Decision, Remarks
<--- Return to Archive