The Economics and Statistics Division maintains archives of previous publications for accountability purposes, but makes no updates to keep these documents current with the latest data revisions from Statistics Canada. As a result, information in older documents may not be accurate. Please exercise caution when referring to older documents. For the latest information and historical data, please contact the individual listed to the right.
<--- Return to Archive
For additional information relating to this article, please contact:
January 11, 2022CURRENT ACCOUNT COMPARISON, 2021Q3 NOTE: For this comparison, all data are sourced from the OECD and are expressed in seasonally adjusted, US Dollars.
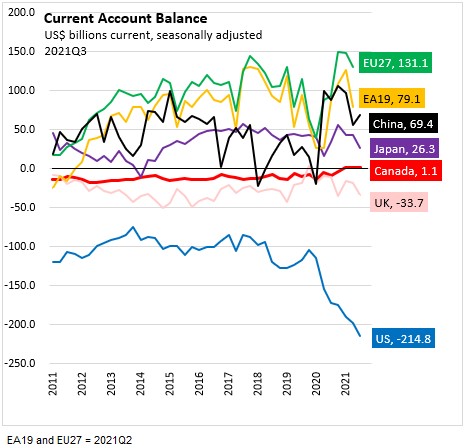
In the third quarter of 2021:
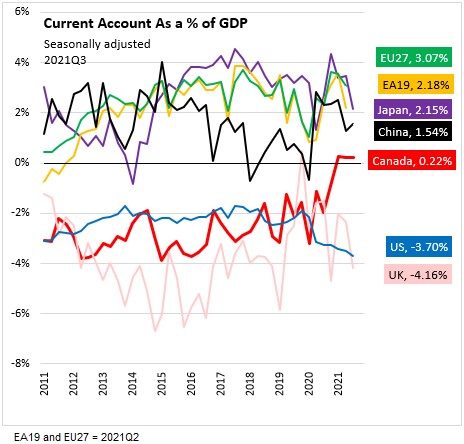
China recorded a current account surplus of $69.4 billion or 1.54% of GDP
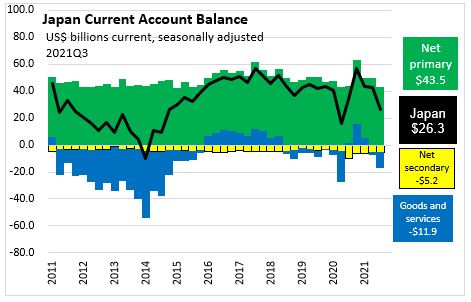
Japan recorded a current account surplus of $26.3 billion or 2.15% of GDP
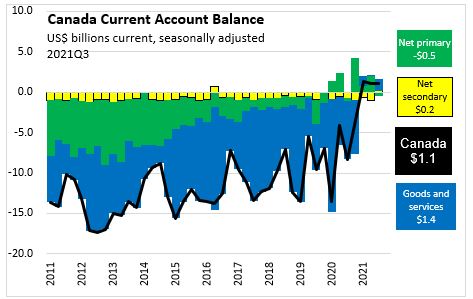
Canada recorded a current account surplus of $1.1 billion or 0.22% of GDP
The United Kingdom recorded a current account deficit of $33.7 billion or -4.16% of GDP
The United States recorded a current account deficit of $214.8 billion or -3.70% of GDP
In the second quarter of 2021:
the European Union recorded a current account surplus of $131.1 billion or 2.18% of GDP
the Euro Area recorded a current account surplus of $79.1 billion or 3.07% of GDP
BALANCE OF PAYMENTS COMPARISON
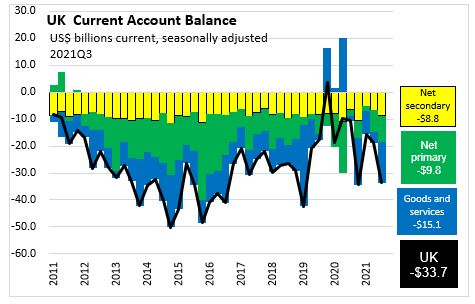


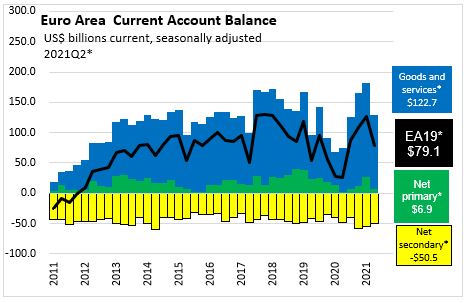
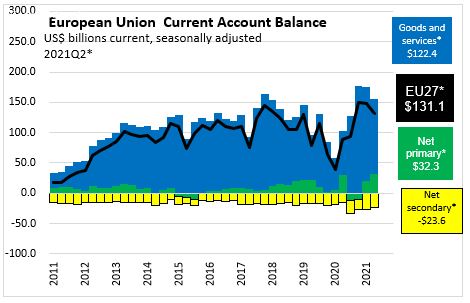
The ratio of the current account balance to the Gross Domestic Product (or % of GDP) provides an indication of the country's trade and income flows relative to the size of the economy.
The ratio is calculated by dividing the net values of exports less imports, primary Income (interest and dividends) and secondary income (transfers) over a period by the gross domestic product for the same period. Although called a ratio, it is usually expressed as a percentage.
A current account surplus indicates upward pressure on the foreign exchange rate unless it is offset by net outflows (leading, acquisition of assets) outside the country the gross domestic product for the same period. Although called a ratio, it is usually expressed as a percentage. A current account surplus indicates upward pressure on the foreign exchange rate unless it is offset by net outflows (leading, acquisition of assets) outside the country.
Source: OECD: Current account Canada; Current account Japan; Current account UK; Current account US; Current account EA19; Current account EU27; Current account China
<--- Return to Archive