The Economics and Statistics Division maintains archives of previous publications for accountability purposes, but makes no updates to keep these documents current with the latest data revisions from Statistics Canada. As a result, information in older documents may not be accurate. Please exercise caution when referring to older documents. For the latest information and historical data, please contact the individual listed to the right.
<--- Return to Archive
For additional information relating to this article, please contact:
September 11, 2025EUROPEAN CENTRAL BANK MONETARY POLICY The European Central Bank (ECB) announced today that it would leave the three key ECB interest rates unchanged. The interest rates on the deposit facility, main refinancing operations and the marginal lending facility will remain at 2.0%, 2.15%, 2.4% respectively.
Global GDP growth is expected to weaken, although less sharply than predicted in the June Projections. Global GDP growth is expected to be 3.3% in 2025, and then to decrease further, to 3.1% in 2026, before recovering to 3.3% in 2027. Global trade growth is expected to slow down in 2025 and further in 2026 with the effect of unwinding frontloading as well as impact from tariffs and policy uncertainty. By 2027, the global trade is expected to recover as US imports rebound. Global headline consumer price index (CPI) inflation is projected to moderate from 4.0% in 2024 to 3.2% in 2025, and then to fall further to 2.9% in 2026 and 2.5% in 2027.
The European economy grew faster than expected in the first quarter of 2025, in part due to frontloading of exports ahead of expected tariffs but started to unwind in the second quarter. Recovery in demand for goods continued, fostered by improving real incomes, while activity in the services sector continued to increase. The Euro Area economy is projected to grow by 1.2% in 2025, revised up from the 0.9% expected in June. The growth projection for 2026 is now slightly lower, at 1.0%, and unchanged to 2027 at 1.3%.
Labour markets have been robust, with rising real incomes and solid private sector balance sheets expected to continue to support consumption. The July unemployment rate was 6.2%. Easing financing conditions are supporting domestic demand, including housing markets, with higher public investment in defence and infrastructure also expected to further support growth. Unemployment rate is estimated to be 6.4% in 2025, 6.3% in 2026 and 6.1% in 2027.
Inflation (HICP) was close to 2.0% through the first half of 2025. New projections estimate that inflation will average 2.1% in 2025, 1.7% in 2026, and 1.9% in 2027. The fall of inflation bellow 2% is influenced by the energy component. Labour cost pressures are easing, with employee unit cost expected to decline through 2027.
The asset purchase programme (APP) and Pandemic Emergency Purchase Programme (PEPP) portfolios are declining at a measured and predictable pace, as the Eurosystem no longer reinvests principal payments from maturing securities.
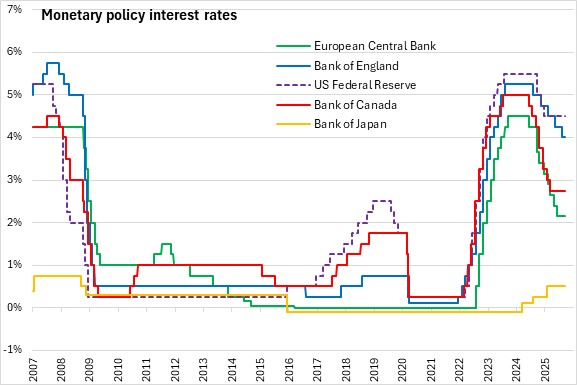
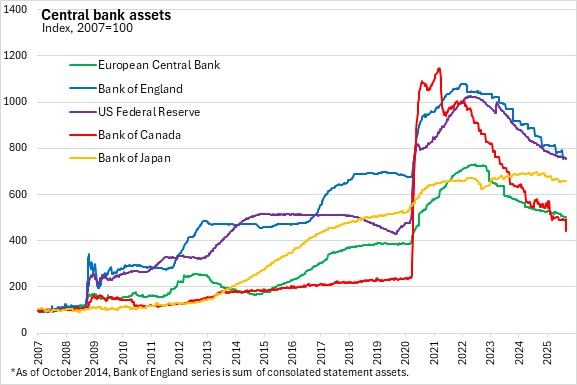
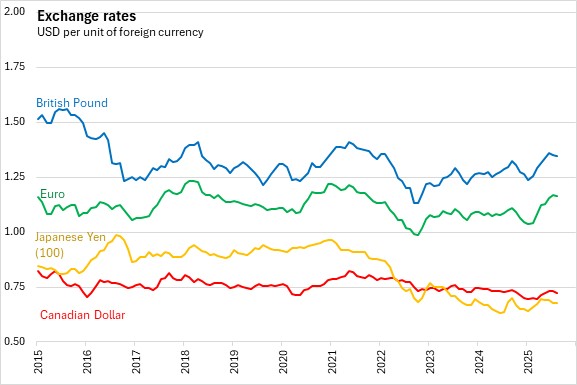
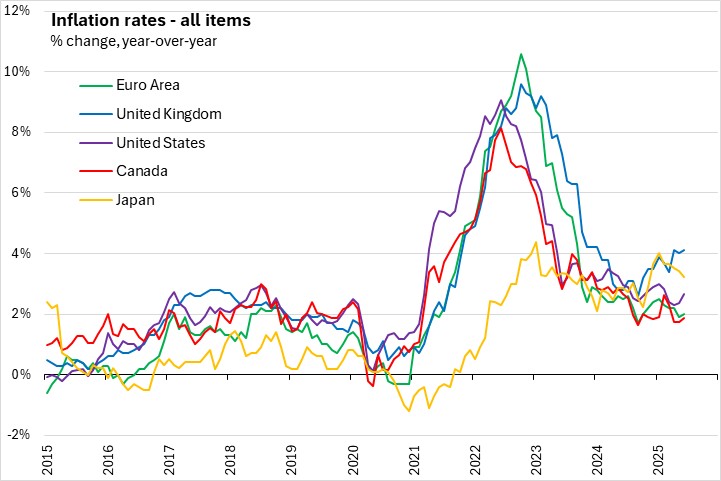
The Governing Council notes it is determined to see inflation sustainably stabilise at its 2.0% medium-term target. The transmission protection Instrument is also available to counter unwarranted, disorderly market dynamics that pose a serious threat to the transmission of monetary policy across all euro area countries, thus allowing the Governing Council to more effectively deliver on its price stability mandate.
The next scheduled monetary policy meeting will be on October 29-30, 2025.
Source: European Central Bank:Monetary policy decisions (Press Release); Press Conference; Monetary Policy Projections (September)
<--- Return to Archive