Forest Vegetation types - CO2
CO2 — White spruce - Balsam fir / Foxberry - Twinflower
Picea glauca - Abies balsamea /Vaccinium vitis-idaea - Linnaea borealis
CO2a — Black crowberry Headland variant
Empetrum nigrum
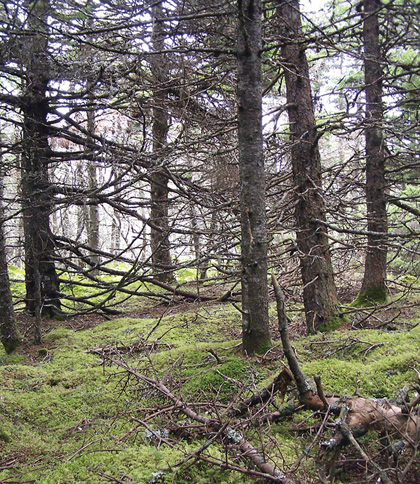 |
Colin's Cove, Richmond County |
Concept: This mid to late successional Vegetation Type (VT) has an overstory dominated by white spruce, with a component of balsam fir. Strong winds, salt spray and harsher climatic conditions, along more exposed headlands and shorelines, often create a severely stunted canopy structure called krummholtz. The CO2a variant defines a krummholtz vegetation type. White spruce - Balsam fir / Foxberry - Twinflower is scattered along the Nova Scotia coast and is typically closer to the shore than other VTs in this group.
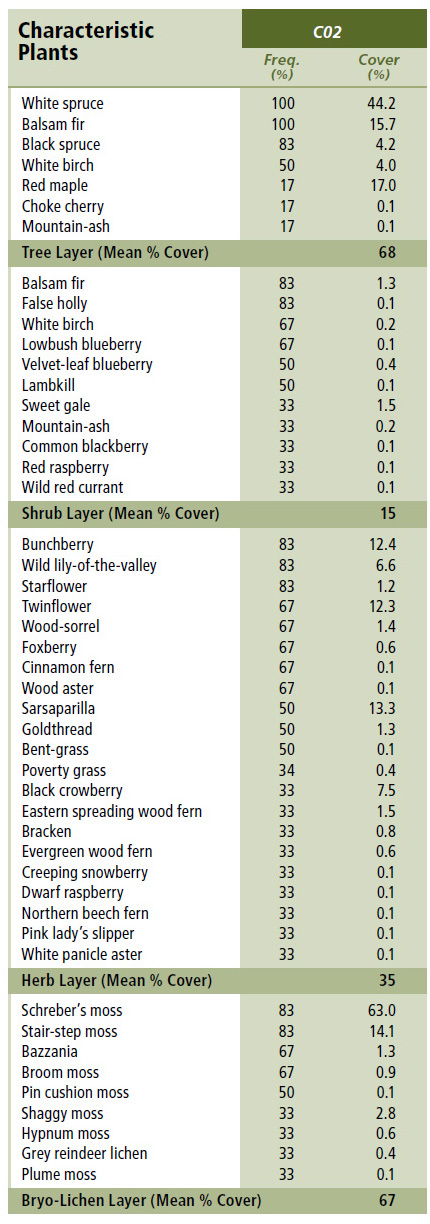
Vegetation: White spruce is the dominant overstory tree along with balsam fir. Black spruce, white birch and red maple are minor associates. The shrub layer is often poorly developed, but includes mountain-ash, wild raisin, false holly, blueberries and lambkill (along with regenerating balsam fir). The well-developed herb layer includes typical upland forest flora such as bunchberry, twinflower, wild lily-of-the-valley, wood sorrel and starflower. For the exposed CO2a variant, ground juniper, sweet gale, bayberry, chokeberry and black crowberry are also common. Schreber's moss and stair-step moss dominate the well-developed bryophyte layer.
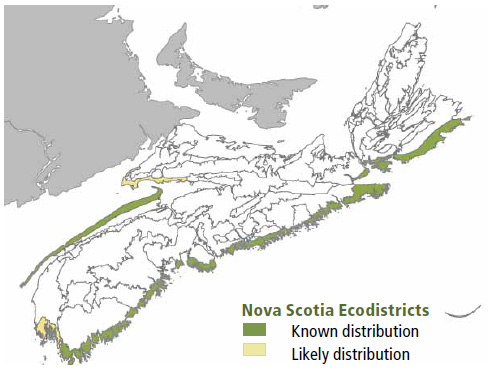
Environmental Setting: CO2 is mainly associated with fresh-moist to moist, nutrient poor to nutrient-medium soils of glacial origin. These soils are generally medium to coarse textured and potentially shallow to bedrock in some locations. This VT is mainly found near shorelines on exposed headlands, hills and ridges, as well as off-shore islands. High winds and salt spray limit tree height potential in this VT, especially in CO2a stands. The VT occurs in more exposed coastal areas of both New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island.
Successional Dynamics: CO2 is a mid to late successional VT dominated by white spruce. On relatively sheltered sites, this even-aged VT typically follows stand-replacing disturbances such as windthrow, breakage and harvesting. CO4 (Balsam fir / Foxberry - Twinflower) may be an earlier successional stage on these sites. On the more exposed CO2a sites, gap or patch disturbance may be more typical because stunted white spruce are less prone to windthrow. CO2a does not tend to shift to other VTs, but does change in development stage. Between stand-level disturbances, natural tree senescence can create uneven age class distribution and other stand structures.
Ecological Features: This closed canopy matrix forest is primarily associated with the Maritime Boreal Atlantic Coastal ecoregion. The forest's longevity is a function of either canopy tree senescence or the frequency of catastrophic stand disturbances (usually hurricanes). Stands close to the coast or on islands are used as nesting sites and roosts for great blue herons and various seabirds. Older stands with balsam fir may host the endangered boreal felt lichen and other uncommon cyanolichens. White spruce is the most salt-tolerant and wind resistant of the native softwood species and acts as a protective belt for balsam fir. Krummholz (trees stunted by severe wind and salt spray exposure) is common at the coastline especially on headlands. Coastal forests are often used by songbirds as they travel along the coast during spring and fall migration.
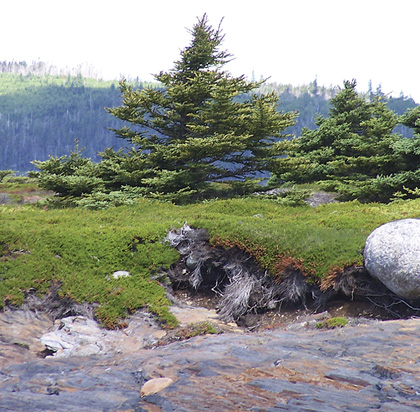 |
| Headland |
Distinguishing Features: Abundant white spruce in the overstory is required to classify this coastal softwood forest. Mountain-ash, heart-leaf birch, foxberry and bazzania are indicators of a coastal influence, though they are not always present. The variant, CO2a, is usually open grown and typical of headlands. Under open conditions black crowberry and common juniper grow in large patches.
| Slope Position: | Middle5 Upper5 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Non - Slightly)7 (Moderately)3 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)8 (Slightly - Moderately)2 |
Elevation Range: |
18 - 58m |
Slope Gradient: |
Gentle6 Moderate2 nd2 |
Aspect: |
East5 West5 |
Exposure: |
Exposed7 Mod. exposed3 |
Microtopography: |
Slightly5 Level3 Moderately2 |
Drainage: |
Moderately well5 Well5 |
Soil Type: |
ST28 ST2-L1 ST81 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till10 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(<30)3 (30-45)7 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(0-5)3 (6-10)5 (11-20)2 |