Forest Vegetation types - CO4
CO4 — Balsam fir / Foxberry - Twinflower
Abies balsamea /Vaccinium vitis-idaea - Linnaea borealis
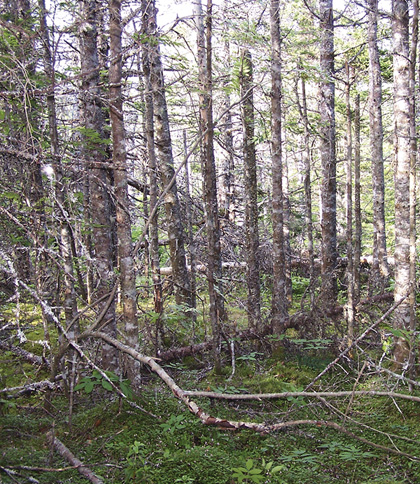 |
Halfway Island Cove, Guysborough County |
Concept: This mid to late successional Vegetation Type (VT) has an overstory dominated by balsam fir. Balsam fir regeneration and moss cover are usually extensive. Balsam fir / Foxberry - Twinflower represents the dominant forest found on fresh/moist, nutrient medium sites along the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia.
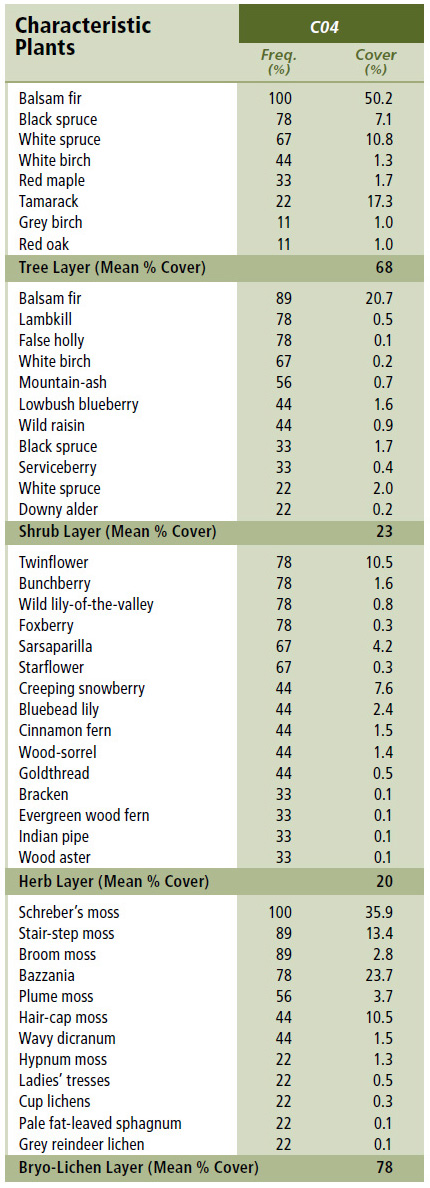
Vegetation: Balsam fir is the dominant overstory tree along with lesser amounts of black spruce and white spruce. Tamarack can also be common on moister sites. Scattered red maple and white birch (if present) are typically in an intermediate canopy position. The shrub layer is dominated by regenerating balsam fir with scattered lambkill, false holly and mountain-ash. Herb layer diversity is low, with frequent bunchberry, wild lily-of-the-valley, sarsaparilla, twinflower and foxberry. Schreber's moss and bazzania dominate the extensive bryophyte layer, along with stair-step moss, broom moss and plume moss.
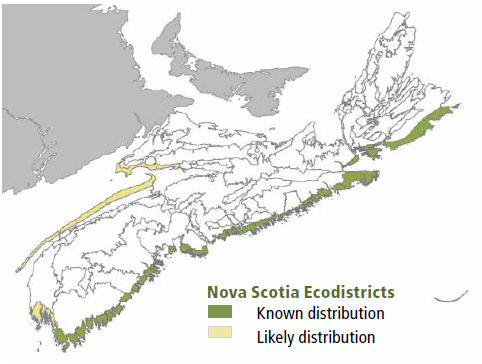
Environmental Setting: CO4 is mainly associated with fresh to fresh-moist, nutrient poor to medium soils of glacial origin. These soils are generally medium to coarse textured and often stony. The majority of this VT is found in the Atlantic Coastal ecoregion. High winds and exposure limit tree height potential in CO4 stands. The VT likely occurs in more exposed coastal areas of both New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island, but has not been documented.
Successional Dynamics: CO4 is a mid to late successional VT dominated by balsam fir. This even-aged VT typically follows stand-replacing disturbances such as windthrow, breakage, insect infestation and harvesting. In the absence of disturbance, the typical lifespan of balsam fir in this ecosystem is 100 years, after which tree senescence will initiate renewal through advanced regeneration. Depending in part on the level of advanced regeneration at time of disturbance, CO4 can perpetuate itself or possibly transition into CO1 (Black spruce - Balsam fir / Foxberry / Plume moss), CO2 (White spruce - Balsam fir / Foxberry - Twinflower) or CO3 (Red spruce / Mountain-ash /Foxberry). Succession to CO1 would be on poorer sites while movement to CO3 would only occur in geographic areas supporting this VT. CO4 may also transition to CO5 (White birch - Balsam fir / Foxberry - Wood aster) on more sheltered sites. Forests that originate after harvesting may initially be dominated by pin cherry, raspberry, white birch and mountain-ash.
Ecological Features: This closed canopy matrix forest is primarily associated with the Maritime Boreal Atlantic Coastal ecoregion. The forest's longevity is a function of either canopy tree senescence or the frequency of catastrophic stand disturbances (usually hurricanes). Both create abundant snags, coarse woody debris, and dense regenerating fir thickets - good cover for small mammals. Stands close to the coast or on islands are used as nesting sites and roosts for great blue herons and some seabirds. Coastal forests are often used by songbirds as they travel along the coast during spring and fall migration. Older stands with balsam fir may have the endangered boreal felt lichen and other uncommon cyanolichens. Mature forests develop abundant old man's beard, a lichen used for nest material by warblers and other species, and winter food for deer foraging on fallen trees.
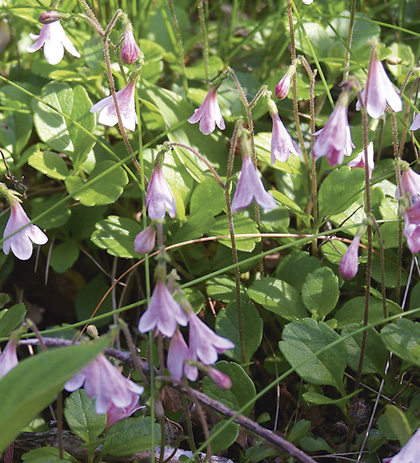 |
| Twinflower |
Distinguishing Features: Balsam fir is the dominant species in this coastal softwood forest. The presence of mountain-ash, heart-leaf birch, foxberry and bazzania are indicators of a coastal influence, though they are not always present. Extensive moss coverage and a thick duff layer characterize the forest floor.
| Slope Position: | Upper5 Level2 Middle2 nd1 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Non - Slightly)4 (Moderately)3 (Very - Excessively)2 nd1 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)9 (Slightly - Moderately)1 |
Elevation Range: |
5 - 41m |
Slope Gradient: |
Gentle7 Level1 Moderate1 Steep1 |
Aspect: |
North3 East2 South3 West1 None1 |
Exposure: |
Exposed8 Mod. exposed2 |
Microtopography: |
Slightly4 Level2 Moderately2 Strongly2 |
Drainage: |
Moderately well6 Well3 Imperfect1 |
Soil Type: |
ST27 ST31 ST151 nd1 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till9 Till/Bedrock1 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(<30)2 (30-45)7 nd1 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(11-20)9 nd1 |