Forest Vegetation types - IH4
IH4 — Trembling aspen / Wild raisin / Bunchberry
Populus tremuloides / Viburnum nudum / Cornus canadensis
 |
Denmark, Colchester County |
Concept: Trembling aspen / Wild raisin / Bunchberry forest is an early successional Vegetation Type (VT) dominated by trembling aspen with a strong component of red maple and balsam fir. This VT has a well-developed understory of disturbance-tolerant woody and herbaceous plants, but reduced bryophyte cover. Trembling aspen / Wild raisin / Bunchberry usually follows stand-replacing disturbances events such as fire, windthrow or clearcutting.
Vegetation: Trembling aspen is the dominant overstory tree, with a lesser component of red maple and balsam fir. White spruce, white birch and red spruce are common canopy associates. The shrub layer is often well developed and includes red maple and balsam fir regeneration as well as woody shrubs like wild raisin, lambkill and blueberry species. A variety of plants can be found in the herb layer, but common species are limited to wild lily-of-the-valley, starflower, bunchberry, twinflower, wood aster and bracken. The bryophyte layer is poorly developed but Schreber's moss and broom moss are usually present.
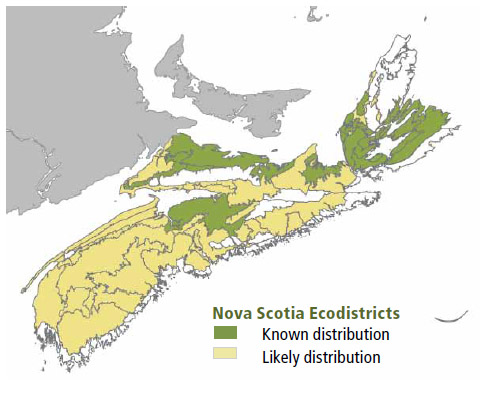
Environmental Setting: IH4 is mainly associated with fresh to moist, nutrient medium soils of glacial origin. This VT is found primarily in the Valley/Central and Northumberland Bras d'Or Lowlands ecoregions. This VT is common on Prince Edward Island and, excluding the highlands, widespread and abundant across much of New Brunswick.
Successional Dynamics: IH4 is an early successional VT that follows stand-level disturbances in both softwood and hardwood forests. Typical disturbance agents include fire, windthrow and harvesting. IH4 stands are usually dominated by even-aged, clonal-origin trembling aspen. Short-lived aspen will deteriorate due to natural senescence, with mortality further accelerated by insect predation, disease and/or wind damage. Possible successional VTs include softwood or mixedwood types such as SH5 (Red spruce – Balsam fir / Schreber's moss), SH6 (Red spruce – Balsam fir / Stair-step moss – Sphagnum) and MW1 (Red spruce – Yellow birch / Evergreen wood fern). On Cape Breton Island MW4 (Balsam fir – Red maple / Wood sorrel – Goldthread) and SH8 Balsam fir / Wood fern / Schreber's moss) are more likely.
Ecological Features:This early successional small patch forest is short lived. Trembling aspen is a very shade-intolerant tree and regenerates primarily through clonal reproduction from root suckers (which may also support large fungal associates such as shoe-string root rot). Aspen colonizes sites rapidly after stand-level disturbances acting as a “nurse crop” for later successional species that tend to grow up through the aspen. This forms two-layered stands before the aspen is overtaken and dies out. Regenerating aspen stands provide cover and forage for many species. Moose and deer feed on its leaves and twigs, ruffed grouse eat its winter buds, snowshoe hare and mice consume its bark and twigs, and beavers make its bark a dietary staple. Resin from aspen buds is the primary source of bee propolis, an essential hive material. Older aspen trees provide soft snags and cavities for several species of birds. Aspen support many species of insects, most notably the forest tent caterpillar, which is an important food for birds and small mammals.
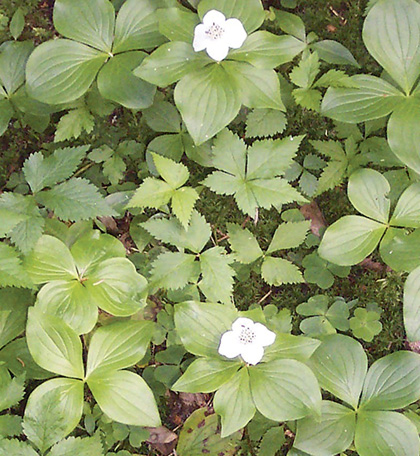 |
| Bunchberry |
Distinguishing Features: These hardwood forests are dominated by trembling aspen with a strong component of red maple and balsam fir. Aspen root suckers are common in the shrub layer.
| Slope Position: | Level5 Upper3 Lower1 Middle1 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Non - Slightly)9 (Moderately)1 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)10 |
Elevation Range: |
14 - 123m |
Slope Gradient: |
Gentle5 Level4 nd1 |
Aspect: |
North1 South3 West2 None4 |
Exposure: |
Moderate10 |
Microtopography: |
Moderately3 Slightly3 Strongly3 Level1 |
Drainage: |
Imperfect5 Moderately well4 Well1 |
Soil Type: |
ST65 ST22 ST31 ST3L1 ST91 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till10 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(<30)1 (30-45)6 (>45)2 nd1 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(0-5)1 (6-10)7 (11-20)1 nd1 |