Forest Vegetation types - SH2
SH2 — Hemlock – White pine / Sarsaparilla
Tsuga canadensis – Pinus strobus /Aralia nudicaulis
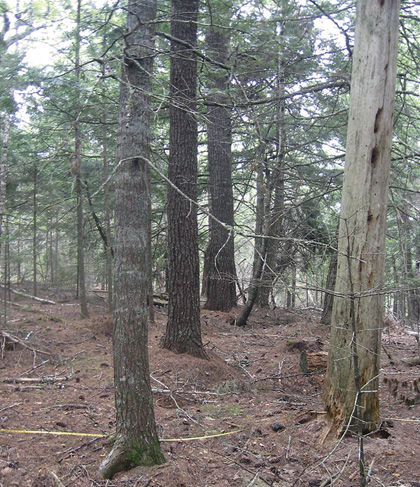 |
4th Christopher Lake, Queens County |
Concept: This late successional Vegetation Type (VT) has an overstory dominated by hemlock and white pine, with minor components of many other species. White pine may occur as a super canopy position. Red spruce presence has been reduced in this VT by partial stand-level disturbances from windthrow, bark beetle and/or harvesting. Due to the long-lived and shade-tolerant nature of the dominant tree species, this VT will develop old forest characteristics that are maintained by gap disturbances. However, infrequent hurricanes and/or fires may periodically renew this VT at a stand-level. SH2 is a typical Acadian softwood VT found on zonal sites that have experienced partial stand-level disturbance.
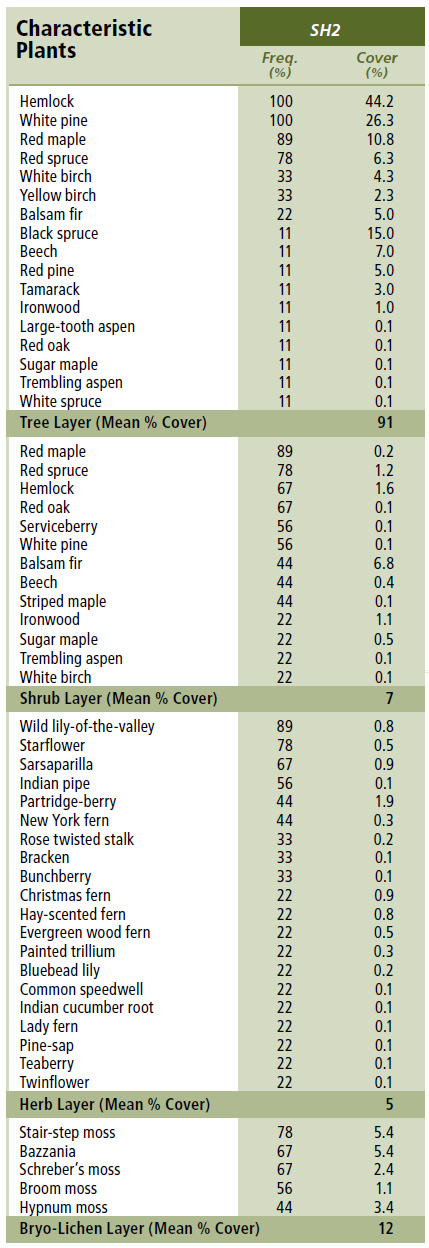
Vegetation: Hemlock and white pine are the dominant overstory trees, with lesser amounts of red spruce, red maple, white birch and balsam fir. The shrub layer is primarily regenerating tree species such as balsam fir, hemlock and red spruce. Regeneration coverage can be extensive depending on crown closure. Herb coverage is usually low and includes typical upland species such as wild lily-of-the-valley, partridge-berry, starflower and sarsaparilla. Schreber's moss, stair-step moss and hypnum moss are common in the bryophyte layer along with bazzania.
Environmental Setting: SH2 is mainly associated with fresh to fresh-moist, nutrient medium soils of glacial origin. This VT can be found throughout mainland Nova Scotia and parts of Cape Breton. However, it is mostly associated with the Western ecoregion because of hemlock's preference for warmer temperatures. Across the Acadian Forest region, most occurrences of this VT are in Nova Scotia. The VT is rare in New Brunswick and unconfirmed for Prince Edward Island.
Successional Dynamics: SH2 is a late successional climatic climax VT dominated by hemlock and white pine and shaped by partial stand-level disturbance. It can develop from several mid-successional VTs including SH5 (Red spruce – Balsam fir / Schreber's moss), SH6 (Red spruce – Balsam fir / Stair-step moss – Sphagnum) and SH8 (Balsam fir / Wood fern / Schreber's moss). This VT develops an uneven-aged structure as it matures with gaps created by the loss of red maple, white birch and balsam fir. These species are replaced by longer-lived hemlock, red spruce, yellow birch and white pine. Between large scale disturbance events SH2 will continue or transition to SH3 (Red spruce – Hemlock / Wild lily-of-the-valley) or SH1 (Hemlock / Pin cushion moss / Needle carpet) through gap replacement.
Ecological Features: This VT typically forms large patches in the Western ecoregion, and small patches elsewhere. The longevity of hemlock and white pine promote old growth development. The oldest forests support lichens, such as coral lichen, indicators of ecological continuity. Hemlock is very shade-tolerant, responding to release after decades of understory suppression, whereas white pine (which has only intermediate shade tolerance) will not thrive for long without release. Mature forests provide large cavity trees, decay resistant snags and coarse woody material and supercanopy pine. This forest may provide cover for moose and deer, and habitat for marten, flying squirrels and various fungi (e.g. hemlock varnish shelf and pine mushrooms). Downed coarse woody debris may provide cover for red-backed salamanders and small mammals, while large trees can provide pileated woodpecker, barred owl and northern goshawk nest sites. Boreal chickadee, pine siskin and both white-winged and red crossbills eat hemlock and white pine seeds. Downy rattlesnake plantain is the only known rare plant.
 |
| Hemlock branch |
Distinguishing Features: Hemlock and white pine (sometimes in a super canopy position) dominate this softwood forest on well drained sites. The forest floor is typically needle carpet with low moss coverage.
| Slope Position: | Level7 Crest1 Lower1 Upper1 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Non - Slightly)7 (Very - Excessively)3 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)9 (Slightly - Moderately)1 |
Elevation Range: |
20 - 114m |
Slope Gradient: |
Level6 Gentle1 Moderate1 Steep1 nd1 |
Aspect: |
North1 South2 West1 None6 |
Exposure: |
Moderate7 Mod. sheltered2 Mod. exposed1 |
Microtopography: |
Slightly5 Moderately2 Strongly2 Severely1 |
Drainage: |
Moderately well7 Well3 |
Soil Type: |
ST26 ST3-L1 ST51 ST61 ST8-C1 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till7 Alluvium1 Colluvium1 nd1 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(30-45)3 (>45)6 nd1 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(0-5)3 (6-10)1 (11-20)5 nd1 |