Forest Vegetation types - SH5
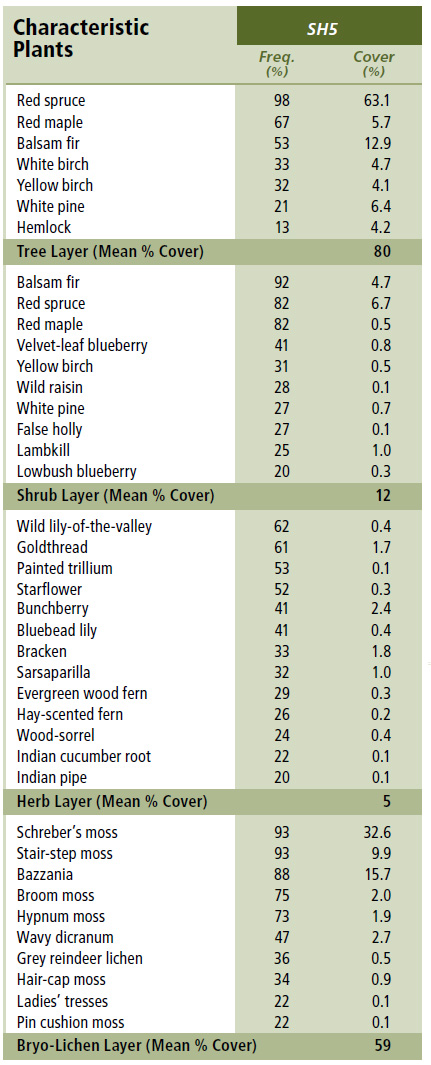
SH5 — Red spruce – Balsam fir / Schreber's moss
Picea rubens – Abies balsamea / Pleurozium schreberi
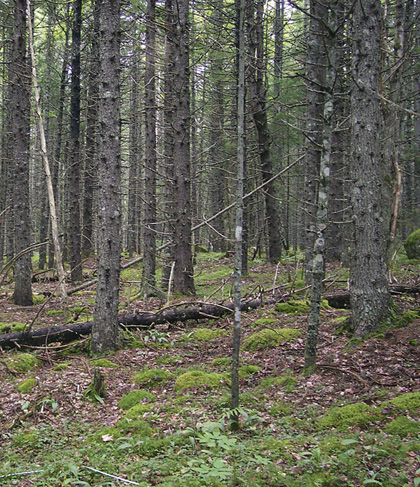 |
Big Indian Lake, Hants County |
Concept: This mid-successional Vegetation Type (VT) has abundant red spruce with varying amounts of balsam fir. Typically minor amounts of red maple and white birch indicate recent disturbance events, whereas yellow birch, white pine and hemlock indicate development toward a later successional stage. Red spruce – Balsam fir / Schreber's moss is a typical Acadian softwood VT found on zonal sites in Nova Scotia.
Vegetation: Red spruce is usually the dominant overstory tree, although balsam fir may be abundant in some stands. Both species are often well represented as regeneration in the shrub layer. Hybrid (red/black) spruce can also be found on more marginal sites. Low light availability often reduces the abundance of common woodland flora such as wild lily-of-the-valley, goldthread and bunchberry. A needle carpet is common under many stands, but coverage by Schreber's moss, stair-step moss and bazzania can be extensive in some.
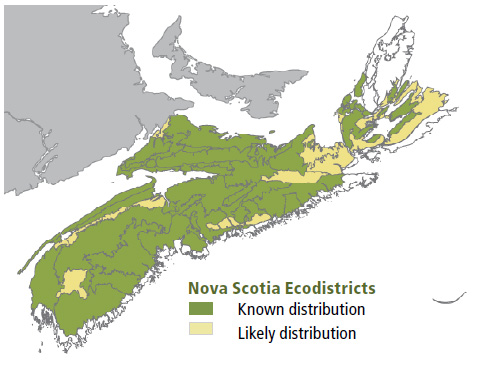
Environmental Setting: SH5 is mainly associated with dry to fresh, nutrient poor to medium soils of glacial origin. These soils are generally medium to coarse textured and often stony. This VT is found throughout mainland Nova Scotia and parts of Cape Breton. It is relatively common in New Brunswick but absent from Prince Edward Island.
Successional Dynamics: SH5 is a predominantly even-aged, mid-successional VT dominated by red spruce. Usually SH5 develops from advanced regeneration present at the time of stand-level disturbance. If advanced regeneration is not present (or has been destroyed), SH5 can also develop from other VTs including IH3 (Large-tooth aspen / Christmas fern – New York fern), IH4 (Trembling aspen / Wild raisin / Bunchberry), IH5 (Trembling aspen – White ash / Beaked hazelnut / Christmas fern), IH6 (White birch – Red maple / Sarsaparilla – Bracken) and MW4 (Balsam fir – Red maple / Wood sorrel – Goldthread). This VT may succeed to later successional types such as SH1 (Hemlock / Pin cushion moss / Needle carpet), SH2 (Hemlock – White pine / Sarsaparilla), SH3 (Red spruce – Hemlock / Wild lily-of-the-valley) and SH4 (Red spruce – White pine / Lambkill / Bracken).
Ecological Features: This closed canopy coniferous forest typically occurs over hundreds of hectares, forming matrix in many ecoregions. Balsam fir and red spruce are very shade-tolerant in the understory. Good seed crops in red spruce start at age 35-45, and the species does not regenerate well before age 50. Forests may provide habitat for marten, spruce grouse, black-backed woodpecker, red and flying squirrels. South facing slopes may provide winter cover for deer. Sapling stage forests are preferred habitat for snowshoe hare. Creeping rattlesnake plantain is the only plant species of conservation concern known from this VT.
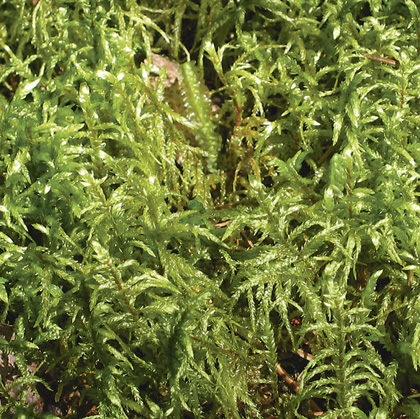 |
| Schreber's moss |
Distinguishing Features: A softwood forest of abundant red spruce with varying amounts of balsam fir occurring on well drained sites. The absence of sphagnum moss (minor amounts in depressions) is diagnostic for identification of this unit.
| Slope Position: | Upper3 Level2 Lower2 Middle2 Other1 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Non - Slightly)6 (Moderately)3 (Very - Excessively)1 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)9 (Slightly - Moderately)1 |
Elevation Range: |
9 - 268m |
Slope Gradient: |
Gentle6 Level2 Moderate1 Other1 |
Aspect: |
North2 East2 South2 West3 None1 |
Exposure: |
Moderate6 Mod. exposed2 Mod. sheltered2 |
Microtopography: |
Moderately5 Slightly2 Strongly2 Other1 |
Drainage: |
Well5 Moderately well3 Imperfect1 Other1 |
Soil Type: |
ST25 ST2-L2 ST61 Other2 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till8 Till/Bedrock1 Other1 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(<30)2 (30-45)4 (>45)3 nd1 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(6-10)3 (11-20)6 nd1 |