Forest Vegetation types - SP3
SP3 — Red Pine – White pine / Bracken – Mayflower
Pinus resinosa – Pinus strobus / Pteridium aquilinum – Epigaea repens
SP3a — Black spruce variant
Picea mariana
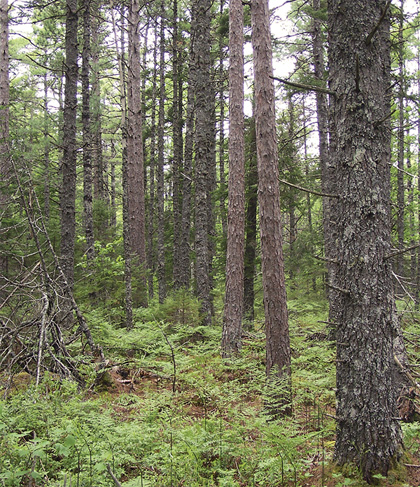 |
Tuskapeake Brook, Annapolis County |
Concept: This early to mid-successional Vegetation Type (VT) has an overstory dominated by both red and white pine. Occurrences co-dominated by black spruce and pine are defined by the SP3a variant. Red Pine – White pine / Bracken – Mayflower usually follows stand-replacing disturbance events such as fire or harvesting.
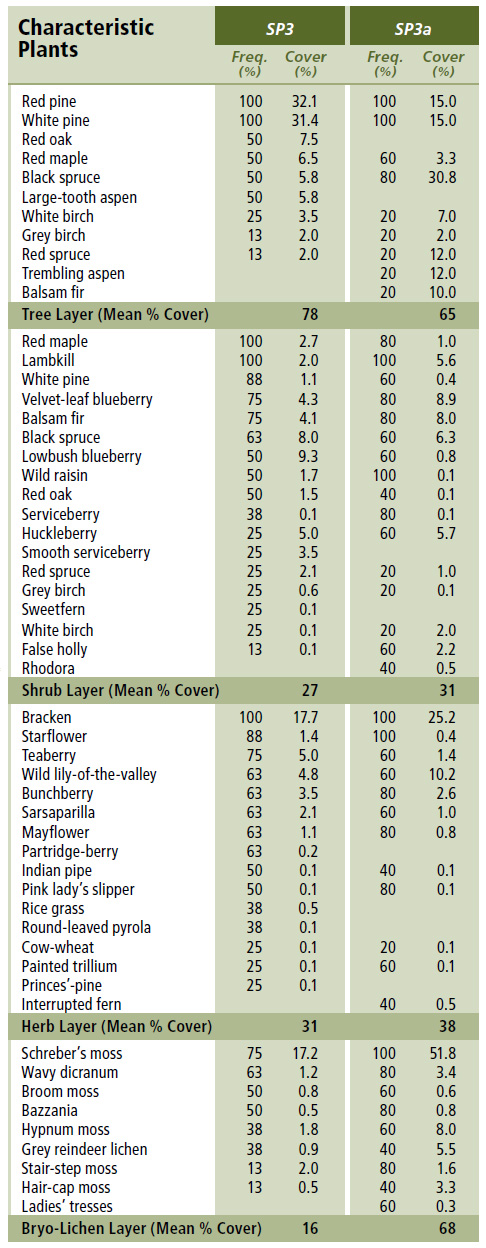
Vegetation: Red and white pine are the dominant overstory trees, usually occurring in similar amounts. Black spruce is the third most common species, with the occasional presence of red maple, large-tooth aspen and red oak. The shrub layer consists mainly of ericaceous species such as lambkill, velvet-leaf blueberry and lowbush blueberry, along with wild raisin. Black spruce and balsam fir regeneration can also be extensive in some stands. Herb layer diversity is relatively low, characterized by species such as pink lady's slipper, mayflower, starflower, bunchberry and sarsaparilla. Bryophyte cover is usually low except in the black spruce variant (SP3a) where heavy cover of Schreber's moss, broom moss and wavy dicranum is common. In dense stands, the forest floor may also be dominated by a needle carpet.
Environmental Setting: SP3 mainly occurs on dry to fresh, nutrient very poor to poor soils. This VT is found throughout mainland Nova Scotia, especially in the Western ecoregion, lowland ecodistricts along the Minas Basin, Annapolis Valley and Northumberland shore. This VT is very rare on Prince Edward Island, and somewhat uncommon in New Brunswick.
Successional Dynamics: Dry, nutrient poor soils and stand-replacing disturbances strongly shape both VT canopy structure and successional patterns. Historically, SP3 stands originated from fire disturbance creating mainly even-aged stands. As the potential impacts of fire are reduced through management white pine and black spruce will increase in dominance, possibly shifting SP3 to SP4 (White pine / Blueberry / Bracken) or directly to SP5 (Black spruce / Lambkill / Bracken), the edaphic climax for this successional pathway.
Ecological Features: This closed or open canopy forest occurs as large patches. Red pine is a shade-intolerant, fire-adapted species whose persistence in this ecosystem will be promoted by fire. Fire scars on residual pine are often found scattered through SP3 stands. White pine is a long-lived species of the Acadian Forest and, as one of the region's largest trees, may provide valuable wildlife habitat for cavity nesting birds such as owls and woodpeckers and mammals such as fishers and porcupines. The acidity (low nutrient content) of the forest floor (due to the abundance of pine needles and ericaceous vegetation) reduces soil fauna, plant diversity, and vertebrate diversity and abundance. Seeds of red pine may provide food for pine siskins, nuthatches and chickadees. Saffron milkcap, is a well-known edible mushroom that forms a mycorrhizal relationship with red pine.
 |
| Mayflower |
Distinguishing Features: Both red pine and white pine need to be present to classify this softwood forest found on dry, nutrient poor soils. The variant SP3a has black spruce co-dominant with the pines.
| Slope Position: | Crest3 Level3 Upper3 Middle1 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Very - Excessively)3 (Moderately)3 (Non - Slightly)2 nd2 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)5 (Slightly - Moderately)2 (Very-Excessively)1 nd2 |
Elevation Range: |
37 - 223m |
Slope Gradient: |
Level5 Gentle3 nd2 |
Aspect: |
North1 East1 South2 West1 None5 |
Exposure: |
Moderate8 Mod. exposed1 nd1 |
Microtopography: |
Slightly4 Moderately3 Level1 nd2 |
Drainage: |
Well5 Imperfect1 Moderately well1 Rapid1 nd2 |
Soil Type: |
ST25 ST11 ST3-G1 ST151 nd2 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till10 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(<30)1 (30-45)2 (>45)3 nd4 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(0-5)1 (6-10)3 (11-20)3 nd3 |