Forest Vegetation types - SP4
SP4 — White pine / Blueberry / Bracken
Pinus strobus / Vaccinium spp. / Pteridium aquilinum
SP4a — Black spruce variant
Picea mariana
SP4b — Huckleberry variant
Gaylussacia baccata
 |
Northeast Lake, Queens County |
Concept: This early to mid-successional Vegetation Type (VT) has an overstory dominated by both red and white pine. Occurrences co-dominated by black spruce and pine are defined by the SP3a variant. Red Pine – White pine / Bracken – Mayflower usually follows stand-replacing disturbance events such as fire or harvesting.
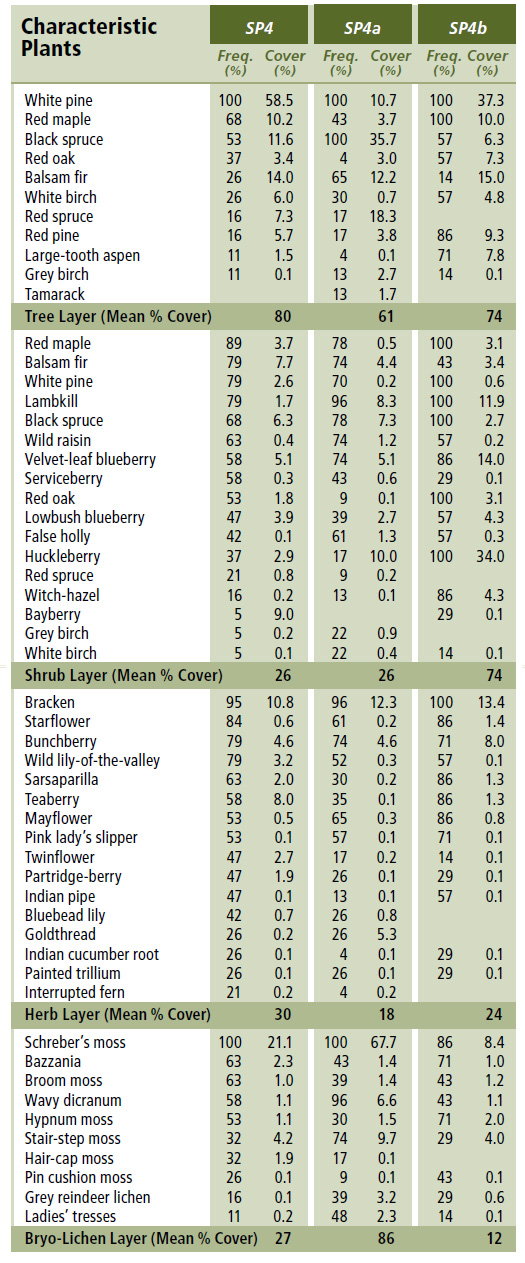
Vegetation: White pine is the dominant overstory tree (often in a super canopy position), along with frequent black spruce. Balsam fir, if present, is limited to the understory and is often damaged by balsam fir woolly adelgid (especially in western Nova Scotia). The shrub layer may be densely occupied by ericaceous species such as lambkill, velvet-leaf blueberry and lowbush blueberry, along with wild raisin and black spruce. Herb layer diversity is relatively low, characterized by species such as bracken, mayflower, teaberry, sarsaparilla and pink lady's slipper. Bryophyte cover is often extensive and includes Schreber's moss, broom moss and wavy dicranum.
Environmental Setting: SP4 occurs on dry to fresh-moist nutrient poor soils. The deep rooting capability of white pine allows this species to access moisture on sites where water deficits occur during the growing season. This VT is usually associated with granitic tills in western Nova Scotia, but can be found scattered throughout the province wherever similar soil types occur. In north central Nova Scotia, SP4 can also be found on finer textured soils. This VT is very rare on Prince Edward Island but relatively common in New Brunswick.
Successional Dynamics: Relatively dry, nutrient poor soils and stand-replacing disturbances strongly shape both VT canopy structure and successional patterns. Historically SP4 stands originated from fire disturbance and are typically even-aged, although scattered white pine can be significantly older due to this species' greater longevity and resistance to windthrow and fire. Earlier successional stages may include a jack pine (SP1) or red pine (SP2) component. Between stand-level disturbance events, senescence and patch disturbances create opportunities for balsam fir, black spruce, red maple, red oak and white birch. This VT can persist for a relatively long time, but stands will eventually succeed to SP5 (Black spruce / Lambkill / Bracken), the edaphic climax for this successional pathway.
Ecological Features: This closed-canopy forest typically forms large patches or matrix ecosystems. White pine has intermediate shade tolerance and may form an understory of young cohorts in early successional red maple, white birch and aspen forests. This life history strategy may reduce tree deformation by the white pine weevil. White pine is a long-lived species (greater than 200 years) of the Acadian Forest and, as one of the region's largest trees, may provide valuable wildlife habitat for cavity nesting birds such as owls and woodpeckers and mammals such as fishers and porcupines. Older pines found in SP4 often have fire scars and frequently contain hollow trunks. Larger white pine may develop a super canopy, increasing susceptibility to lightning strikes, especially on higher relief. The acidity (low nutrient content) of the forest floor (due to the abundance of pine needles and ericaceous vegetation) reduces soil fauna, plant diversity, and vertebrate diversity and abundance. Following fire, the decay-resistant snags may stand for many decades, providing perch and cavity sites in the new forest.
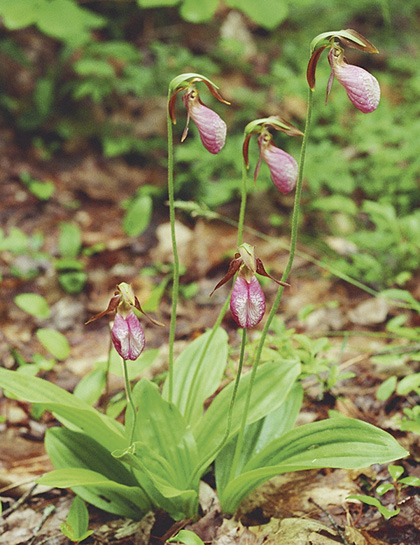 |
| Pink lady's slipper (Reg Newell) |
Distinguishing Features: This is a softwood forest dominated by white pine with lesser amounts of black spruce and red maple. Variant SP4a has dominant black spruce. Variant SP4b exhibits high cover to huckleberry in the understory. Lambkill and blueberry are common.
| Slope Position: | Level3 Middle3 Upper3 Other1 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Non - Slightly)6 (Very - Excessively)3 (Moderately)1 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)8 (Slightly - Moderately)2 |
Elevation Range: |
13 - 207m |
Slope Gradient: |
Gentle6 Level3 Other1 |
Aspect: |
North3 East1 South2 West1 None3 |
Exposure: |
Moderate9 Other1 |
Microtopography: |
Slightly5 Level2 Moderately2 Strongly1 |
Drainage: |
Well5 Moderately well2 Imperfect1 Other2 |
Soil Type: |
ST23 ST12 ST32 ST2-L1 ST15-L1 ST61 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till9 Glaciofluvial1 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(<30)2 (30-45)3 (>45)4 nd1 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(0-5)1 (6-10)6 (11-20)3 |