Forest Vegetation types - TH6
TH6 — Red oak – Yellow birch / Striped maple
Quercus rubra – Betula alleghaniensis / Acer pensylvanicum
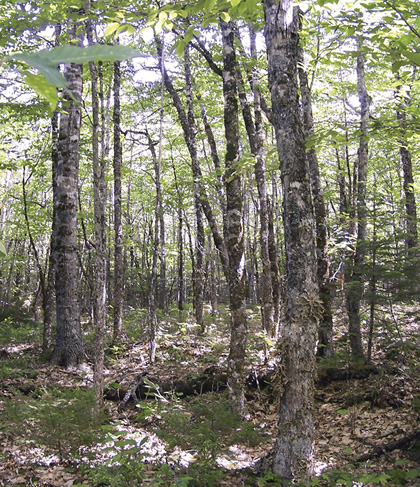 |
Baker Settlement, Lunenburg County |
Concept: This mid to late successional Vegetation Type (VT) has an overstory dominated by red oak and yellow birch with lesser amounts of other species. Red oak's co-dominance with other hardwoods defines this VT. Due to the long-lived and shade-tolerant nature of dominant overstory trees, TH6 can develop old forest characteristics that are maintained by gap disturbance. However disturbance regimes associated with this VT are variable.
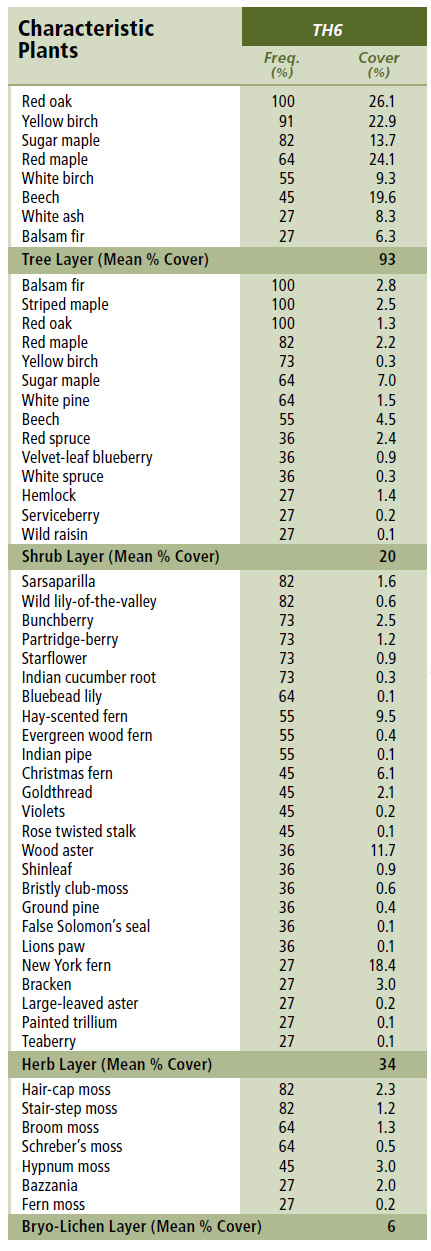
Vegetation: Red oak and yellow birch are the dominant overstory trees, with lesser amounts of sugar maple and/or red maple. Scattered beech, balsam fir, white birch, red spruce and white pine are also common. The shrub layer contains regenerating tree species (especially red oak) along with striped maple. Balsam fir can be locally abundant, but the balsam fir woolly adelgid often keeps this species from advancing into the overstory. A diverse and extensive herb layer is characterized by sarsaparilla, Indian cucumber root, partridge-berry, bunchberry and hay-scented fern. The bryophyte later is discontinuous and species-poor, especially where the forest floor is characterized by leaf litter and/or where the softwood component is low.
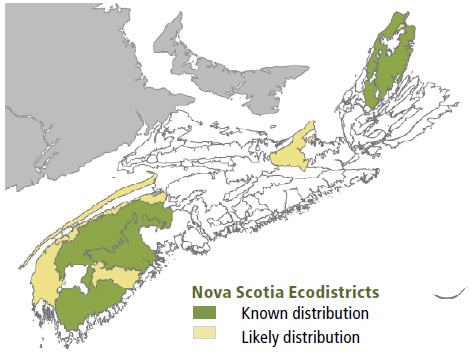
Environmental Setting: TH6 is mainly associated with dry to moist, nutrient medium soils of glacial origin. It occurs primarily on the upper and middle slopes of gentle to hilly terrain in the Western ecoregion, but may be scattered elsewhere. It is uncommon in New Brunswick and very rare on Prince Edward Island.
Successional Dynamics: TH6 is a mid to late successional hardwood VT that may have even-aged or uneven-aged structure, depending on disturbance history. The mechanism for maintenance of red oak in this VT is not fully understood, although low-intensity spring fires are thought to play a role. Increased presence of red maple and/or white birch generally indicates more intense past disturbances. Early successional stages can include IH4 (Trembling aspen / Wild raisin – Bunchberry) and IH6 (White birch – Red maple / Sarsaparilla – Bracken). On drier sites, TH6 may be the climax VT, while on more mesic sites TH6 may succeed to TH1 (Sugar maple / Hay-scented fern) or TH2 (Sugar maple / New York fern – Northern beech fern) in the absence of fire.
Ecological Features: In western Nova Scotia, this forest is distributed as a large patch spanning several hundred hectares. Longevity and high shade tolerance promote old growth potential. Beech scale disease, introduced from Europe in the 1890s, has decimated the beech component of these stands and reduced mast production. This forest may provide habitat for warblers, thrushes, woodpeckers, flying squirrels and fishers. Large trees may provide nest sites for barred owls and northern goshawks, while downed coarse woody debris can provide cover for red-backed salamanders and small mammals. Hard mast from beech, oak and beaked hazelnut provides significant food for bears, squirrels, chipmunks, small mammals and birds. Oak regeneration is favoured as browse by deer. Generally oak regeneration performs poorly in the understory unless enhanced by fire. Oak is the preferred host of maitake, or hen-of-the-woods, a prized edible mushroom. Black trumpet mushrooms may also be found as mycorrhizal partners with oak and beech.
 |
| Cancer root |
Distinguishing Features: Red oak and at least one northern hardwood species (yellow birch, sugar maple, beech) in the upper canopy of this hardwood forest is diagnostic for classification. TH6 forest is typical of western Nova Scotia and usually found on drier soils than the other TH forests.
| Slope Position: | Upper5 Middle3 Crest1 Level1 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Non - Slightly)4 (Moderately)4 (Very - Excessively)2 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)10 |
Elevation Range: |
50 - 201m |
Slope Gradient: |
Gentle6 Steep2 Level1 Moderate1 |
Aspect: |
North3 East3 South3 None1 |
Exposure: |
Moderate5 Exposed2 Mod. exposed2 Mod. Sheltered1 |
Microtopography: |
Moderately3 Strongly3 Level2 Severely1 Ultra1 |
Drainage: |
Well7 Moderately well2 Rapid1 |
Soil Type: |
ST24 ST2-G2 ST82 ST11 ST2-L1 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till5 Colluvium2 nd3 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(<30)1 (30-45)5 (>45)3 nd1 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(0-5)4 (6-10)4 (11-20)1 nd1 |