Forest Vegetation types - TH8
TH8 — Red maple – Yellow birch / Striped maple
Acer rubrum – Betula alleghaniensis /Acer pensylvanicum
TH8a —White ash variant
Fraxinus americana
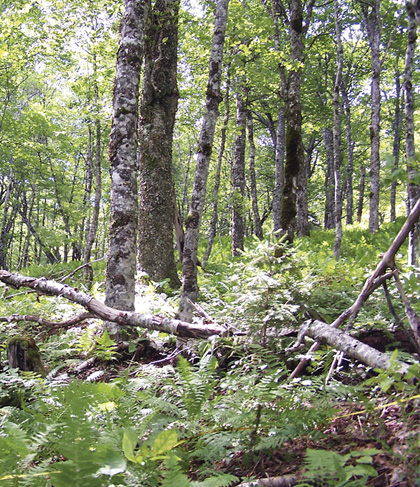 |
Twin Lakes, Guysborough County |
Concept: This mid to late successional Vegetation Type (VT) has an overstory dominated by red maple and yellow birch. Sugar maples are noticeably absent or only present as a minor structural component. The variant (TH8a) defines stands where white ash is present in the overstory, a reflection of increased moisture and/or fertility. In the eastern mainland, TH8 is a late successional VT; elsewhere in Nova Scotia it is considered mid-successional.
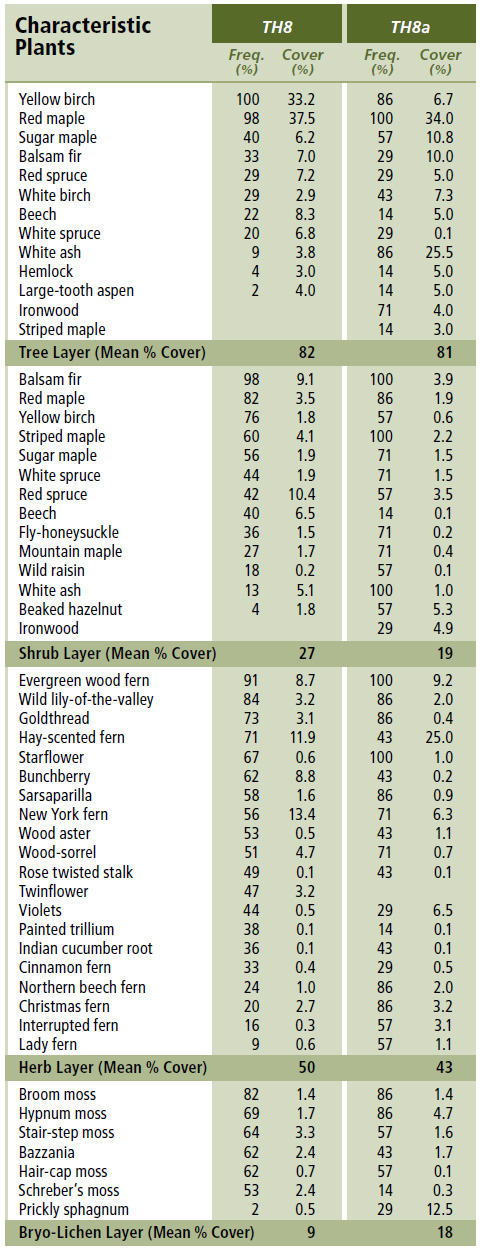
Vegetation: Red maple and yellow birch are the dominant overstory trees, but most stands also have a minor softwood component comprised of balsam fir, red spruce and/or white spruce. In the shrub layer these roles reverse with softwood regeneration dominant (especially balsam fir). Other shrubs include striped maple, mountain maple and fly-honeysuckle. The herb layer has extensive fern cover including wood ferns, hay-scented fern and New York fern. Other common plants include bunchberry, wood sorrel and gold thread. The bryophyte later is discontinuous and species-poor, especially where the forest floor is characterized by leaf litter and/or where the softwood component is low.
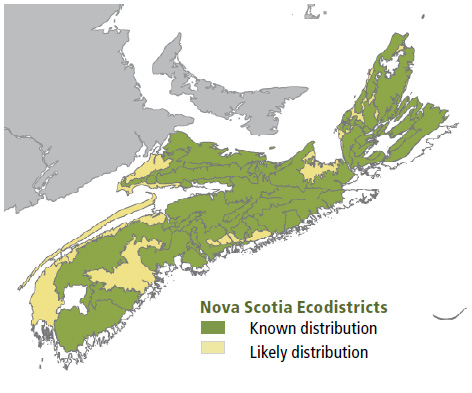
Environmental Setting: TH8 is mainly associated with fresh to fresh-moist, nutrient medium to rich soils of glacial origin. It is found primarily in eastern Nova Scotia on upper and middle slopes of gentle terrain and on the drumlins of the Eastern Interior, Mulgrave Plateau and Bras d'Or Lowlands ecodistricts. However, it can be found scattered throughout Nova Scotia on similar sites. This VT is widespread and common throughout the Acadian Forest Region.
Successional Dynamics: TH8 is a mid to late successional climatic climax hardwood VT dominated by red maple and yellow birch. Stands are predominantly even-aged but can develop uneven-aged canopy structures with time. Disturbance agents include wind, ice damage, insects/disease and harvesting. In eastern Nova Scotia, early successional VTs include IH4 (Trembling aspen / Wild raisin / Bunchberry), IH6 (White birch – Red maple / Sarsaparilla – Bracken) and IH7 (Red maple / Hay-scented fern – Wood sorrel). Early successional stages can be by-passed if, at the time of disturbance, advanced red maple and yellow birch regeneration is retained. In the Nova Scotia Uplands ecoregion where sugar maple occurs, later successional VTs include TH1 (Sugar maple / Hay-scented fern) and TH2 (Sugar maple / New York fern – Northern beech fern).
Ecological Features: Across eastern Nova Scotia, this closed canopy hardwood forest is distributed as a large patch spanning several hundred hectares. Yellow birch's longevity and shade tolerance facilitates the development of uneven-aged stand structures. The tree can produce stems 25 meters tall with diameters of up to 100 cm, and has the ability to withstand severe crown breakage and rotting. Large diameter, living, hollow trees are common in this forest type and provide good denning opportunities, cavity nest sites for songbirds, and nest sites for broad-winged hawks and northern goshawks. Downed coarse woody debris may provide cover for red-backed salamanders and small mammals. Yellow birch is an abundant source of seed during the winter for many species of birds and small mammals, while red maple is an important early spring pollen source. Birch trees may be deformed by birch cinder conch, a fungal growth occasionally harvested for Chaga tea.
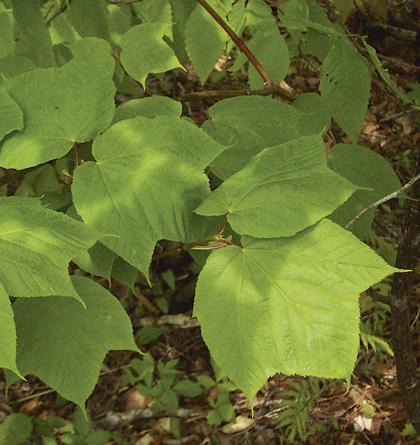 |
| Striped maple |
Distinguishing Features: This forest is common in eastern Nova Scotia on well drained upper slopes. The absence or sparse cover of sugar maple and beech is diagnostic. Evergreen wood fern is typically the most abundant fern, although New York can also be locally extensive.
| Slope Position: | Upper4 Middle3 Level2 Other1 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Non - Slightly)4 (Moderately)4 (Very - Excessively)2 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)9 (Slightly - Moderately)1 |
Elevation Range: |
19 - 286m |
Slope Gradient: |
Gentle6 Moderate2 Other1 nd1 |
Aspect: |
North3 East3 South2 West1 None1 |
Exposure: |
Moderate4 Mod. exposed4 Exposed1 Sheltered1 |
Microtopography: |
Moderately4 Strongly3 Slightly2 Other1 |
Drainage: |
Moderately well4 Well4 Imperfect2 |
Soil Type: |
ST23 ST2-L3 ST61 ST81 Other2 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till9 Other1 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(<30)1 (30-45)5 (>45)3 nd1 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(0-5)2 (6-10)6 (11-20)1 nd1 |